
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Sampleincomestatement-d92415c1850943f99cad74a3cb3bbf20.jpg)
This type of COGS accounting may apply to car manufacturers, real estate developers, and others.ĭepending on the COGS classification used, ending inventory costs will obviously differ.Running a business involves a lot of hidden costs. Costs can be directly attributed and are specifically assigned to the specific unit sold. Specific identification is special in that this is only used by organizations with specifically identifiable inventory. Thus, for the three units sold, COGS is equal to $18.75. In the above example, the weighted average per unit is $25 / 4 = $6.25. This is multiplied by the actual number of goods sold to find the cost of goods sold. Under weighted average, the total cost of goods available for sale is divided by units available for sale to find the unit cost of goods available for sale. Under LIFO, COGS would consist of the last three units produced, totaling $10 x 1 + $5 x 2 = $20. Under FIFO, COGS would consist of the first three units produced, totaling $5 x 3 = $15. In the subsequent period, the company sold three units.

However, due to rising material prices, the last unit costs $10 to produce. The first three units cost $5 to produce. For example, assume that a company purchased materials to produce four units of their goods. Under FIFO, COGS consists of finished inventory units that were produced first and thus consist of costs incurred first, whereas under LIFO, COGS consists of finished inventory units that were produced last and therefore consists of later or most recent costs. Very briefly, there are four main valuation methods for inventory and cost of goods sold. IFRS and US GAAP allow different policies for accounting for inventory and cost of goods sold. It helps management and investors monitor the performance of the business. It doesn’t reflect the cost of goods that are purchased in the period and not being sold or just kept in inventory. The basic purpose of finding COGS is to calculate the “true cost” of merchandise sold in the period. These costs will fall below the gross profit line under the selling, general and administrative (SG&A) expense section. They may also include fixed costs, such as factory overhead, storage costs, and depending on the relevant accounting policies, sometimes depreciation expense.ĬOGS does not include general selling expenses, such as management salaries and advertising expenses. For goods, these costs may include the variable costs involved in manufacturing products, such as raw materials and labor. COGS is deducted from revenue to find gross profit.Ĭost of goods sold consists of all the costs associated with producing the goods or providing the services offered by the company.
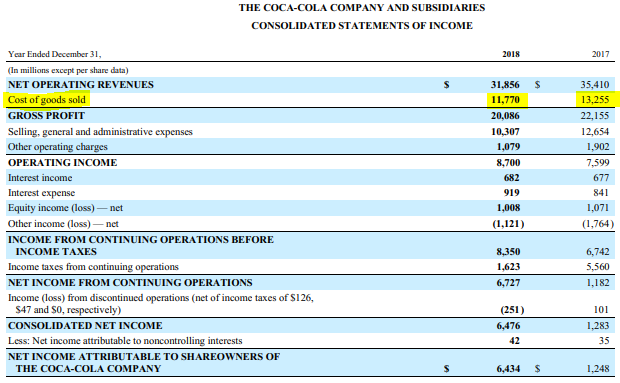
COGS is often the second line item appearing on the income statement, coming right after sales revenue. It includes material cost, direct labor cost, and direct factory overheads, and is directly proportional to revenue.Īs revenue increases, more resources are required to produce the goods or service. Updated What is Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)?Ĭost of Goods Sold (COGS) measures the “ direct cost” incurred in the production of any goods or services.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
